What Are the Early Signs of Tinnitus That Often Go Unnoticed?
Tinnitus affects millions of people worldwide, yet many dismiss its early warning signs as temporary annoyances or normal aging processes. Recognizing the subtle indicators of this auditory condition can be crucial for timely intervention and improved quality of life. From faint ringing sounds that appear during quiet moments to intermittent buzzing that seems to come and go, understanding what to watch for can help you take proactive steps toward managing this often misunderstood condition.
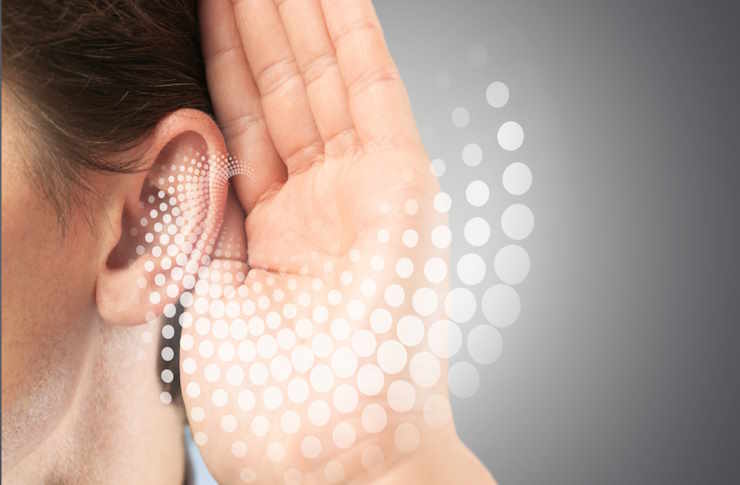

Many people experience unusual sounds in their ears but fail to recognize them as potential signs of tinnitus. This condition, characterized by perceiving sound without an external source, can manifest in ways that are easy to overlook or attribute to other causes. Understanding these early indicators is essential for seeking appropriate care and preventing potential progression.
Common Symptoms Associated With Tinnitus
Tinnitus presents itself through various auditory sensations that differ from person to person. The most frequently reported symptom is a persistent ringing sound, but this condition can also manifest as buzzing, hissing, whistling, or even roaring noises. These sounds may be constant or intermittent, affecting one or both ears.
Many individuals notice these sounds primarily in quiet environments, such as when trying to fall asleep or during moments of silence. The volume can range from barely perceptible to loud enough to interfere with concentration and daily activities. Some people experience pulsatile tinnitus, where the sound synchronizes with their heartbeat, creating a rhythmic pulsing sensation.
Early signs often include brief episodes of ringing that last only a few seconds or minutes, which many people dismiss as insignificant. However, when these episodes become more frequent or prolonged, they may indicate developing tinnitus that warrants attention.
Understanding The Connection Between Hearing Loss And Tinnitus
The relationship between hearing loss and tinnitus is significant and well-documented in medical literature. Research indicates that approximately 90 percent of tinnitus cases occur alongside some degree of hearing impairment. This connection stems from damage to the tiny hair cells in the inner ear, which are responsible for transmitting sound signals to the brain.
When these hair cells become damaged due to aging, noise exposure, or other factors, the brain may compensate for the reduced auditory input by creating phantom sounds. This explains why many people with hearing loss also experience tinnitus symptoms. The condition can affect individuals of any age, though it becomes more prevalent with advancing years.
Early signs of this connection include difficulty hearing conversations in noisy environments, frequently asking others to repeat themselves, or noticing that certain frequencies sound muffled. When these hearing challenges coincide with unusual ear sounds, the likelihood of tinnitus increases substantially.
Expert Insights On Early Diagnosis Of Tinnitus
Healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of early detection for effective management of tinnitus. Audiologists and ear, nose, and throat specialists recommend seeking evaluation when unusual ear sounds persist for more than a few days or begin to interfere with daily functioning.
During diagnostic assessments, medical professionals typically conduct comprehensive hearing tests, review medical history, and examine the ear structures. They may also perform imaging studies if they suspect underlying conditions contributing to the symptoms. Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention strategies that can prevent the condition from worsening or becoming more disruptive.
Experts note that many patients delay seeking help because they assume nothing can be done about tinnitus. However, modern approaches offer various management options that can significantly improve quality of life, making early professional consultation valuable.
Lifestyle Changes That May Alleviate Tinnitus Symptoms
Implementing certain lifestyle modifications can help manage tinnitus symptoms and potentially reduce their intensity. Reducing exposure to loud noises is fundamental, as excessive noise can worsen the condition. Using ear protection in noisy environments and keeping volume levels moderate when using headphones are practical preventive measures.
Stress management techniques, including meditation, yoga, and regular exercise, have shown promise in helping individuals cope with tinnitus. Stress often exacerbates symptoms, creating a cycle that lifestyle changes can help break. Adequate sleep, maintaining a balanced diet, and limiting caffeine and alcohol consumption may also contribute to symptom relief.
Sound therapy, which involves using background noise or specialized devices to mask tinnitus sounds, can provide relief for many people. White noise machines, nature sounds, or soft music can make the phantom sounds less noticeable, particularly during quiet moments.
When To Seek Professional Help For Tinnitus
Knowing when to consult a healthcare provider is crucial for proper tinnitus management. Immediate medical attention is warranted if tinnitus appears suddenly, affects only one ear, or is accompanied by dizziness, hearing loss, or ear pain. These symptoms could indicate underlying conditions requiring prompt treatment.
You should also seek professional help if tinnitus persists for more than a week, interferes with sleep or concentration, or causes significant emotional distress. Mental health impacts, including anxiety and depression, can develop when tinnitus remains unaddressed, making timely intervention important.
Healthcare providers in your area can offer comprehensive evaluations and develop personalized management plans. Local services may include audiology clinics, ENT specialists, and hearing centers equipped to diagnose and treat tinnitus effectively. Early consultation increases the likelihood of successful symptom management and prevents potential complications.
Recognizing Subtle Warning Signs
Beyond the obvious auditory symptoms, tinnitus can present through less apparent indicators. Some people experience increased sensitivity to everyday sounds, a condition called hyperacusis, which often accompanies tinnitus. Others notice changes in how they perceive certain frequencies or develop difficulty focusing in environments with background noise.
Temporary changes in hearing after exposure to loud events, such as concerts or sporting events, may signal early damage that could lead to persistent tinnitus. Paying attention to these subtle shifts in auditory perception allows for earlier intervention and better outcomes. Keeping a journal of when symptoms occur, their duration, and any associated factors can provide valuable information for healthcare providers during evaluation.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.