Step-by-Step Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms and Treatment: Early Signs, Diagnosis, and Relief Options
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and potential long-term damage. Understanding its early signs and available treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively. This comprehensive guide walks you through the essential aspects of RA, from initial symptoms to current treatment approaches.
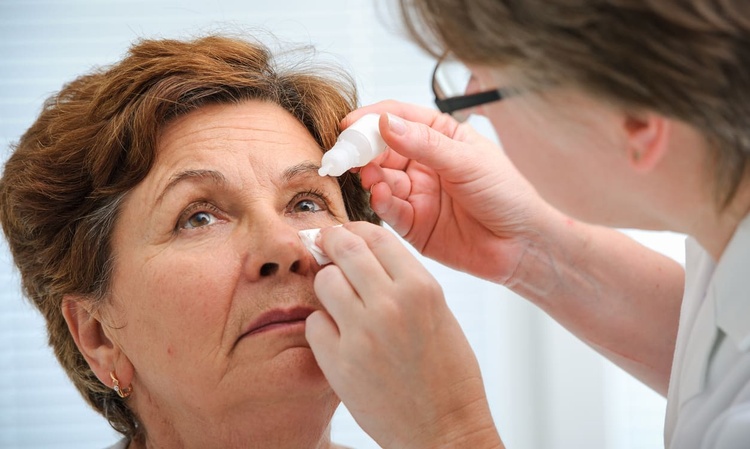

What Are the Early Warning Signs of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
The earliest signs of rheumatoid arthritis often begin subtly and may be easily overlooked. Common initial symptoms include morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes, particularly in small joints of the hands and feet. Symmetrical joint pain, meaning both sides of the body are affected similarly, is another characteristic sign. Fatigue, low-grade fever, and general malaise may also accompany these symptoms. Early recognition and intervention are crucial for better outcomes.
How Is Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing RA involves several steps and tests. Your healthcare provider will typically start with a thorough physical examination and medical history review. Blood tests checking for rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies are common diagnostic tools. Imaging tests, including X-rays, MRI, and ultrasound, help assess joint damage and monitor disease progression. Early diagnosis is essential for preventing joint destruction and managing symptoms effectively.
What Are the Major Risk Factors and Triggers?
Several factors can increase your risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Gender plays a significant role, with women being two to three times more likely to develop RA than men. Age (typically onset between 40-60 years), genetics, and smoking are other significant risk factors. Environmental triggers like infections, stress, and certain medications may initiate symptoms in susceptible individuals. Understanding these factors helps in prevention and management strategies.
What Current Treatment Options Are Available?
Treatment for RA typically involves a multi-faceted approach. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) like methotrexate are often prescribed as first-line treatments. Biological response modifiers, newer medications that target specific parts of the immune system, may be recommended for moderate to severe cases. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids help manage pain and inflammation. Physical therapy and occupational therapy are also crucial components of comprehensive treatment.
Which Lifestyle Changes Can Help Manage Symptoms?
Making specific lifestyle modifications can significantly impact RA management. Regular low-impact exercise helps maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, can help reduce inflammation. Stress management techniques, adequate rest, and proper joint protection strategies are essential. Some people find complementary therapies like acupuncture or massage helpful for symptom relief.
What Are the Associated Costs and Treatment Options?
| Treatment Type | Estimated Monthly Cost | Insurance Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| DMARDs | $100-$500 | Generally covered |
| Biological Response Modifiers | $1,000-$3,000 | Partial coverage common |
| Physical Therapy | $50-$100 per session | Often limited coverage |
| NSAIDs | $20-$50 | Usually covered |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Managing rheumatoid arthritis requires a long-term commitment to treatment and lifestyle modifications. While the condition cannot be cured, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help prevent joint damage and maintain quality of life. Regular monitoring and adjusting treatment plans as needed ensure the best possible outcomes for individuals living with RA.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.