Discover Top Foods That Help Control Diabetes: A Guide to Diabetic Friendly Eating and Sugar Control
Managing diabetes through diet is a cornerstone of effective blood sugar control. Understanding which foods can help regulate glucose levels while providing essential nutrients is crucial for anyone living with diabetes. This comprehensive guide explores the most beneficial foods and dietary strategies to help maintain stable blood sugar levels and promote overall health.
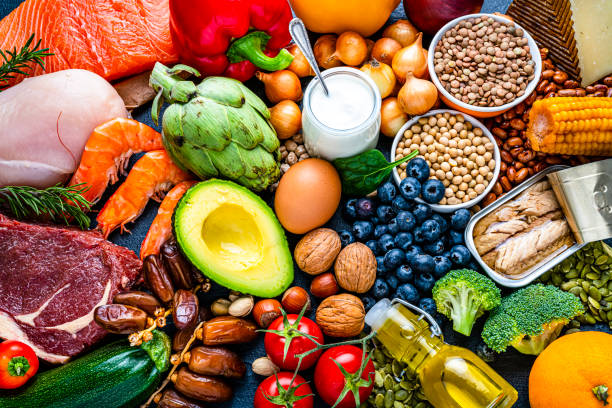

How Does Diet Impact Blood Sugar Control?
The foods we consume directly affect blood glucose levels, making dietary choices crucial for diabetes management. Carbohydrates have the most significant impact, as they break down into glucose during digestion. However, not all carbohydrates are created equal. Complex carbohydrates, fiber-rich foods, and those with a low glycemic index cause smaller, more gradual changes in blood sugar compared to simple carbohydrates and sugary foods.
Which Foods Are Best for Diabetic Blood Sugar Management?
Non-starchy vegetables top the list of diabetes-friendly foods. Options like leafy greens, broccoli, carrots, and peppers are high in fiber and nutrients while having minimal impact on blood sugar. Lean proteins such as chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes help maintain steady glucose levels while providing essential nutrients. Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats offer sustained energy release due to their complex carbohydrate content.
What Are the Most Effective Low-Glycemic Food Choices?
Foods with a low glycemic index (GI) are excellent choices for blood sugar control. These include:
-
Berries and citrus fruits
-
Steel-cut oats and barley
-
Sweet potatoes and winter squash
-
Greek yogurt and cottage cheese
-
Nuts and seeds
-
Beans and lentils
How Should Diabetics Plan Their Meals for Optimal Blood Sugar Control?
Successful meal planning involves balancing portions and timing. The plate method suggests filling half your plate with non-starchy vegetables, quarter with lean protein, and quarter with complex carbohydrates. Eating regular, properly portioned meals helps prevent blood sugar spikes and crashes. Including a combination of protein, fiber, and healthy fats in each meal helps slow down glucose absorption.
What Are Expert-Recommended Strategies for Diabetic Nutrition?
Nutrition experts emphasize the importance of consistency in meal timing and portion control. They recommend:
-
Eating every 4-5 hours during waking hours
-
Including protein with each meal and snack
-
Limiting processed foods and added sugars
-
Monitoring carbohydrate intake
-
Staying hydrated with water
-
Reading nutrition labels carefully
What Diabetic-Friendly Foods Are Available in Regular Grocery Stores?
Most supermarkets offer numerous diabetes-friendly options across different departments:
| Department | Recommended Foods | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Produce | Leafy greens, berries, citrus | High fiber, low GI, rich in nutrients |
| Protein | Fish, chicken, tofu, eggs | Blood sugar stabilization |
| Dairy | Greek yogurt, cheese | Protein-rich, minimal impact on glucose |
| Pantry | Nuts, seeds, whole grains | Healthy fats, complex carbs |
| Frozen | Vegetables, fruit without added sugar | Convenience, portion control |
Prices for diabetic-friendly foods vary by region and season. Generally, fresh produce costs $2-5 per pound, while protein sources range from $3-10 per pound. Whole grains typically cost $1-4 per pound.
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Managing diabetes through diet requires consistent attention to food choices and meal planning, but with the right knowledge and strategy, it’s achievable. Focus on whole, minimally processed foods while monitoring portion sizes and meal timing to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.