Curious About Medicare Meal Delivery? Discover Eligibility and Benefits
Medicare meal delivery programs provide essential nutritional support for eligible beneficiaries who face challenges preparing meals independently. These services can significantly improve health outcomes and quality of life for seniors and individuals with specific medical conditions. Understanding the eligibility requirements, available benefits, and how these programs support overall health is crucial for those considering this valuable Medicare benefit.
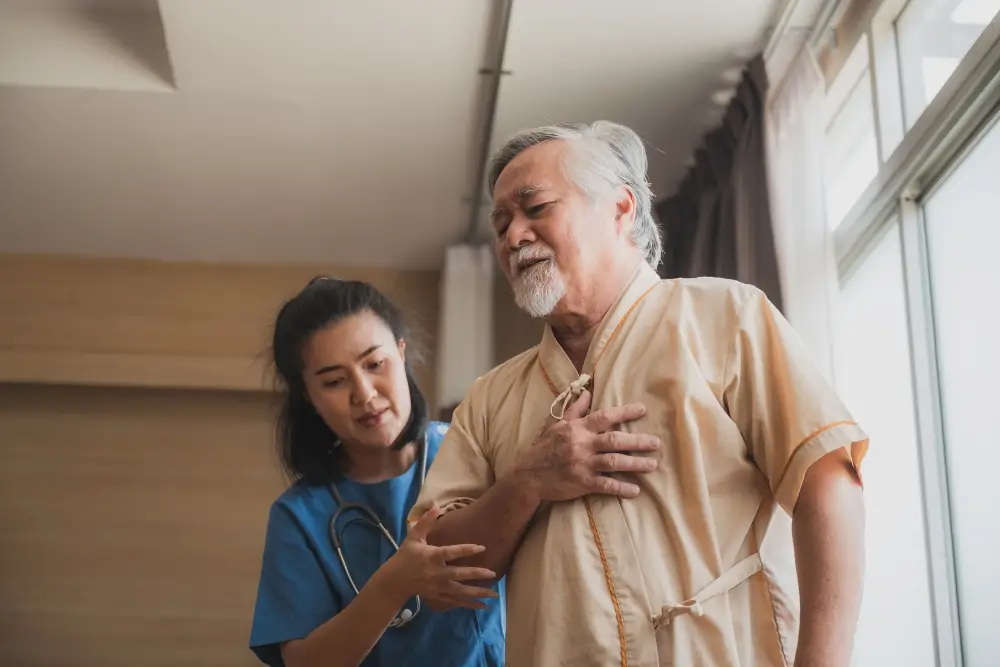

Medicare meal delivery services represent a vital healthcare benefit that extends beyond traditional medical coverage. These programs recognize that proper nutrition plays a fundamental role in maintaining health, preventing complications, and supporting recovery from illness or injury. For many Medicare beneficiaries, accessing nutritious meals can become challenging due to mobility limitations, chronic conditions, or post-hospitalization recovery periods.
Understanding Medicare Meal Delivery Programs
Medicare meal delivery operates through various channels, primarily Medicare Advantage plans and certain Medicare supplement programs. Unlike traditional Medicare Parts A and B, which focus on hospital and medical services, meal delivery benefits typically fall under Medicare Part C (Medicare Advantage) or specialized programs designed to address social determinants of health. These services acknowledge that nutrition directly impacts medical outcomes and healthcare costs.
The meals provided through these programs are carefully planned by registered dietitians and often tailored to specific dietary requirements. Recipients may receive frozen, fresh, or shelf-stable meals delivered directly to their homes on a regular schedule. The frequency and duration of meal delivery depend on individual needs, medical conditions, and the specific program guidelines.
Who Qualifies for Meal Delivery Services?
Eligibility for Medicare meal delivery varies depending on the specific program and Medicare plan. Generally, beneficiaries must meet certain criteria related to their health status, living situation, or recent medical events. Common qualifying conditions include recent hospital discharge, diagnosis of chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease, limited mobility that affects meal preparation, or living alone without adequate support systems.
Medicare Advantage plans may offer meal delivery as a supplemental benefit, with eligibility determined by the plan’s specific guidelines. Some programs require a physician’s referral or assessment by a healthcare professional to determine medical necessity. Additionally, certain state Medicaid programs that coordinate with Medicare may provide meal delivery services for dual-eligible beneficiaries who meet income and health criteria.
Post-acute care situations often trigger meal delivery benefits, particularly following hospital stays or skilled nursing facility discharge. These temporary benefits typically last for a specified period, such as two weeks to three months, depending on the individual’s recovery needs and plan provisions.
How Meal Delivery Supports Health and Recovery
Meal delivery programs serve multiple health-supporting functions beyond basic nutrition. For individuals managing chronic conditions, specially designed meals can help control blood sugar levels, reduce sodium intake, or provide heart-healthy options that support medical treatment plans. This targeted nutritional support can prevent complications and reduce the likelihood of hospital readmissions.
The convenience factor also plays a crucial role in health maintenance. When beneficiaries no longer need to shop for groceries or prepare meals, they can focus energy on recovery, medication management, and following other aspects of their care plans. This is particularly valuable for individuals with limited mobility, cognitive challenges, or those recovering from surgery or illness.
Meal delivery services also provide peace of mind for family members and caregivers who may worry about their loved one’s nutritional intake. Regular meal delivery ensures consistent access to balanced nutrition, which supports immune function, wound healing, and overall strength during recovery periods.
| Provider | Service Type | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Mom’s Meals | Frozen meal delivery | $6-8 per meal |
| Silver Cuisine | Fresh meal delivery | $12-15 per meal |
| Medicare Advantage Plans | Covered benefit | $0-50 copay per delivery |
| Meals on Wheels | Community-based | $3-7 per meal |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The integration of meal delivery into healthcare represents a growing recognition of nutrition’s role in medical outcomes. Studies have shown that beneficiaries who receive meal delivery services experience fewer emergency room visits, reduced hospital readmissions, and improved medication adherence. This holistic approach to healthcare addresses not just immediate medical needs but also the underlying factors that contribute to health and wellness.
For those interested in accessing meal delivery through Medicare, the first step involves reviewing current Medicare plan benefits or speaking with a Medicare advisor during open enrollment periods. Medicare Advantage plans often highlight meal delivery as a supplemental benefit, making it easier for beneficiaries to identify available options. Additionally, healthcare providers can provide referrals or assessments that may qualify individuals for these services.
Medicare meal delivery programs represent an innovative approach to healthcare that recognizes the connection between nutrition and medical outcomes. By providing convenient access to nutritious meals, these services support recovery, manage chronic conditions, and improve overall quality of life for eligible beneficiaries. Understanding eligibility requirements and available options helps Medicare beneficiaries make informed decisions about incorporating meal delivery into their healthcare plan.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.